Fusarium avenaceum
Overview
|
Scientific name
|
Fusarium avenaceum |
|
Genus
|
Fusarium |
|
EPPO code
|
GIBBAV |
|
Common name
|
Cereal foot rot |
|
Synonyms
|
Gibberella avenacea |
Description
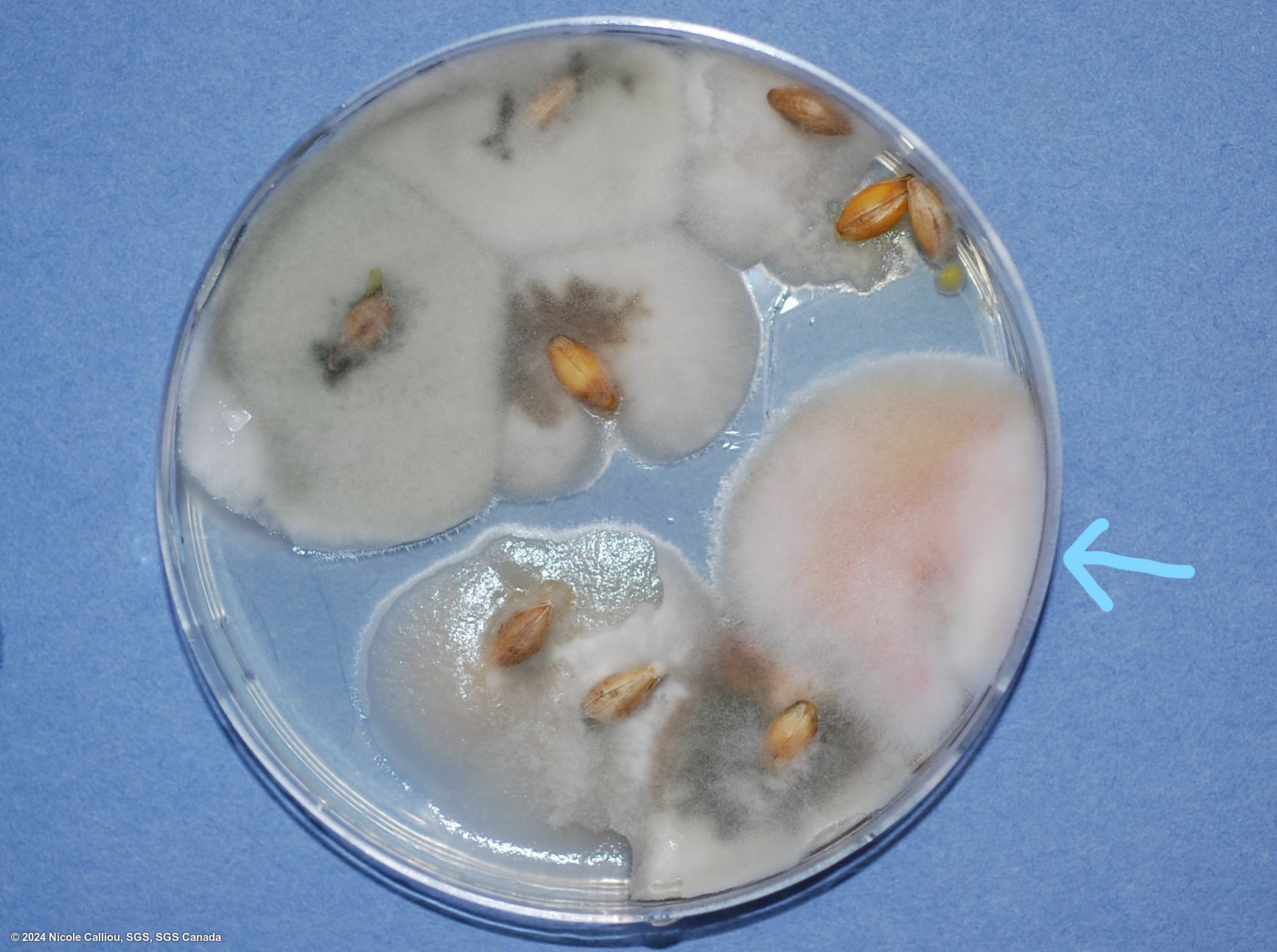
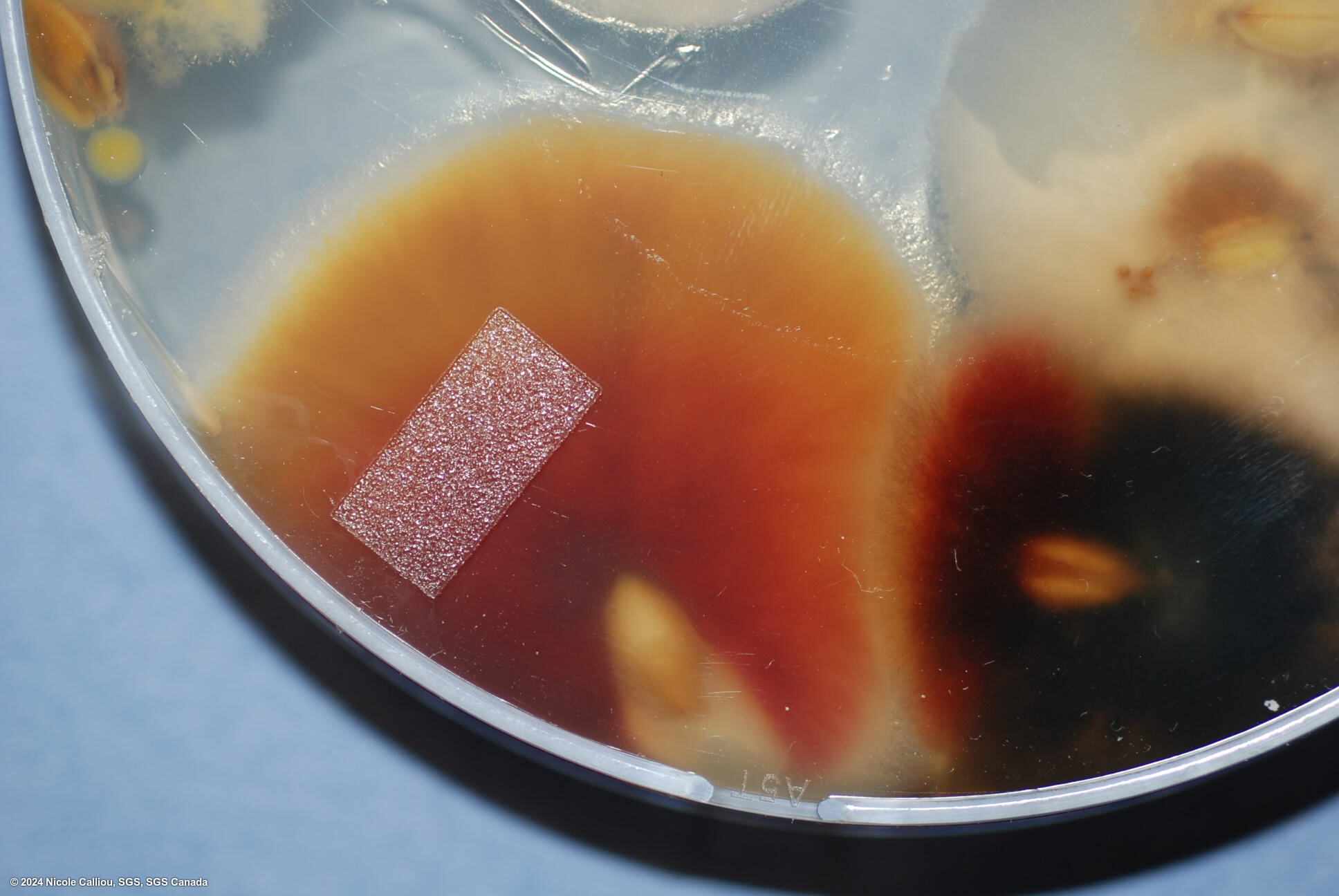
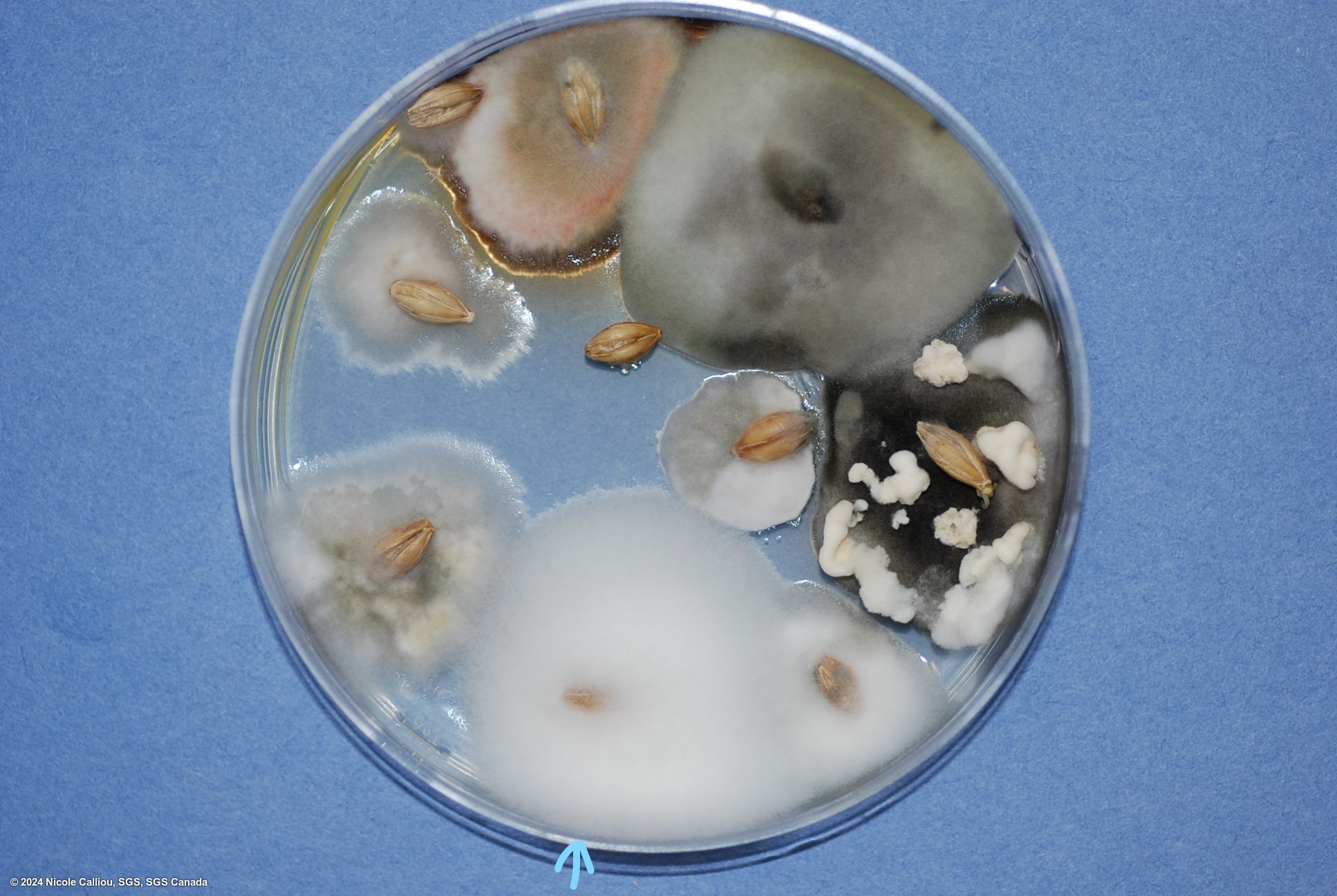
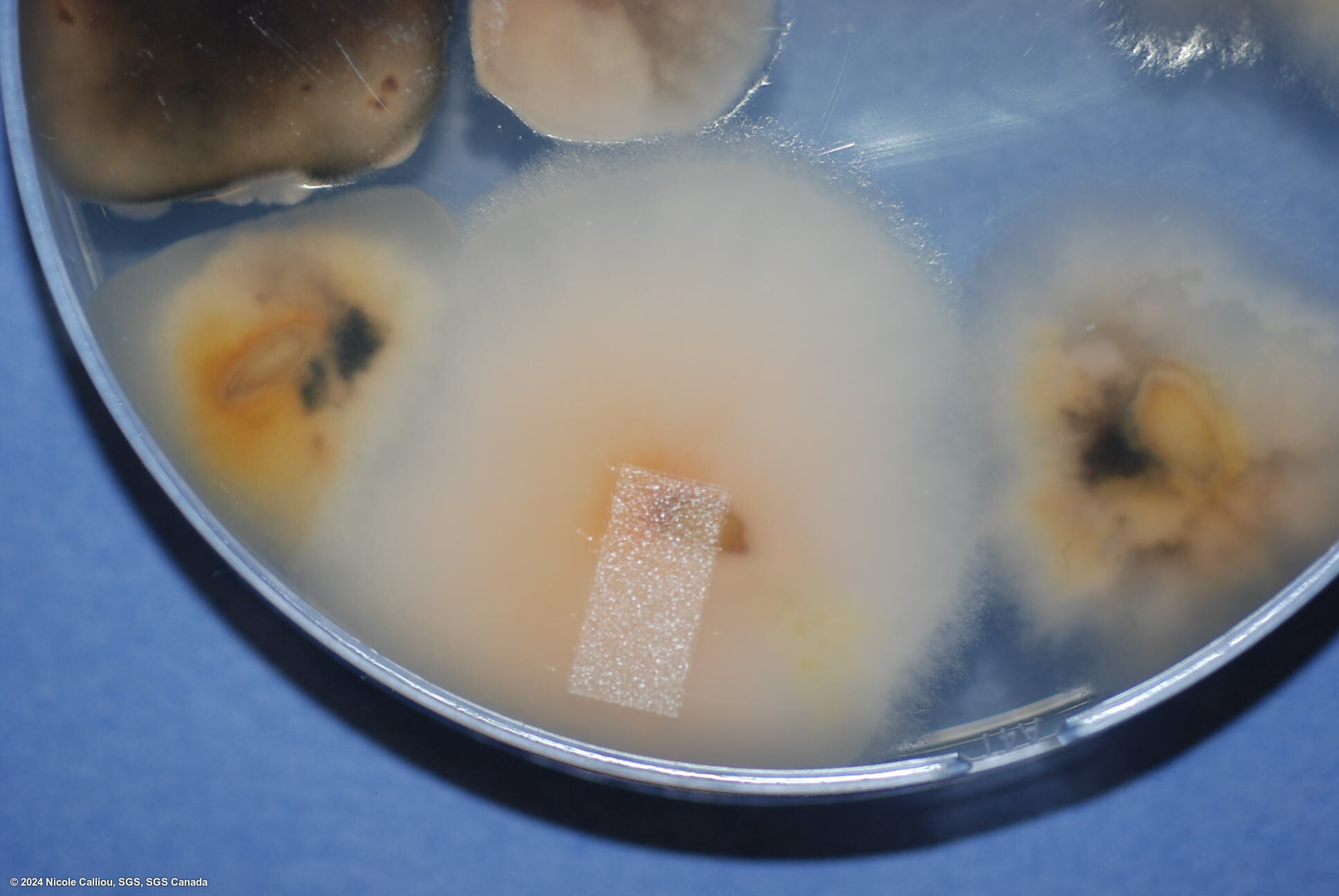
On PDA, growth can vary from slow to somewhat rapid, the aerial mycelium is dense and often white, but frequently varies in color from yellow or tan, to pink, red or brown. Often the description published is 'grayish rose.' The under surface colouration varies from yellow or tan to carmine red to dark brown. Orange sporodochia may form on colonies originating from seed, depending on growth conditions. Sporodochia form quite often in the center of the colony on pure cultures.
On Malt agar, the mycelium is abundant and aerial, yellow to pink coloured, somtimes cream white. Sporodochia are orange, concentrated in the center of the colony.
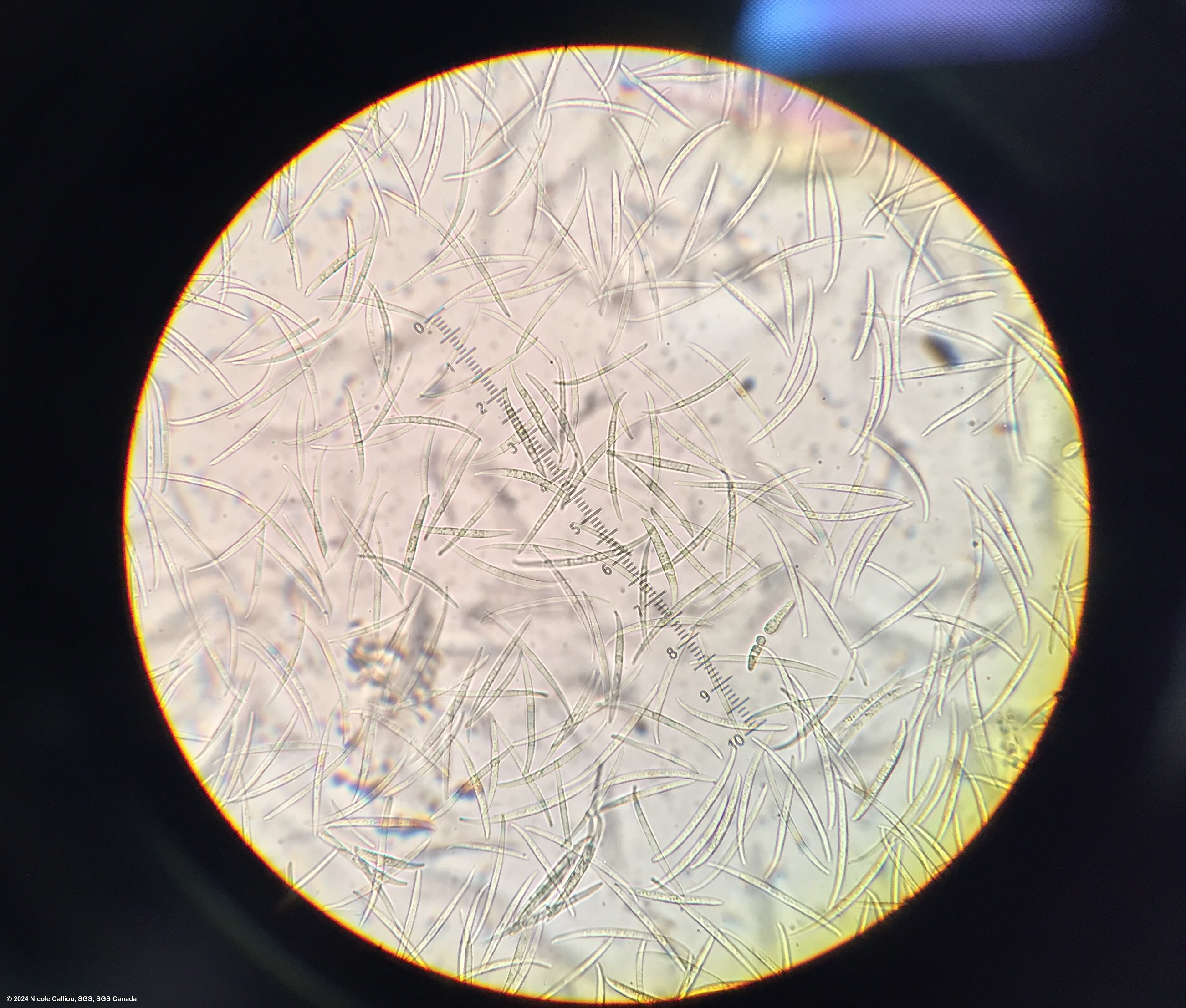
Conidiophores: Unbranched and branched monophialides. Macroconidia are very long, slender, thing walled with a basal cell foot-shaped and an apical cell elongated that may be bent. Microconidia (cigar-shaped) are very rare in dark conditions and may be observedd with NUV light. Mixed sizes of conidia, micro- and macro-, are observed from sporodochia on isolates on PDA, but on CLA only macroconidia true to type are observed. Chlamydospores are absent.
From ISTA's Common Laboratory Seed Health Testing Methods for Detecting Fungi:
The fungus forms pinnotes which are bright orange to almost red. They are produced in patches on a mycelial mat, sometimes formed in long rows on seed, often surrounded by white mycelium.
Conidia slender, hyaline, falcate, with 3-6 but usually 5-septa, 28-72 x 2.5-4μm. In slide preparations, conidia often stick together.