Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris
Overview
|
Scientific name
|
Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris |
|
Genus
|
Xanthomonas |
|
EPPO code
|
XANTCA |
|
Common name
|
Black Rot |
|
Synonyms
|
Bacillus campestris |
Description
Descriptions from ISTA 7-019a method:
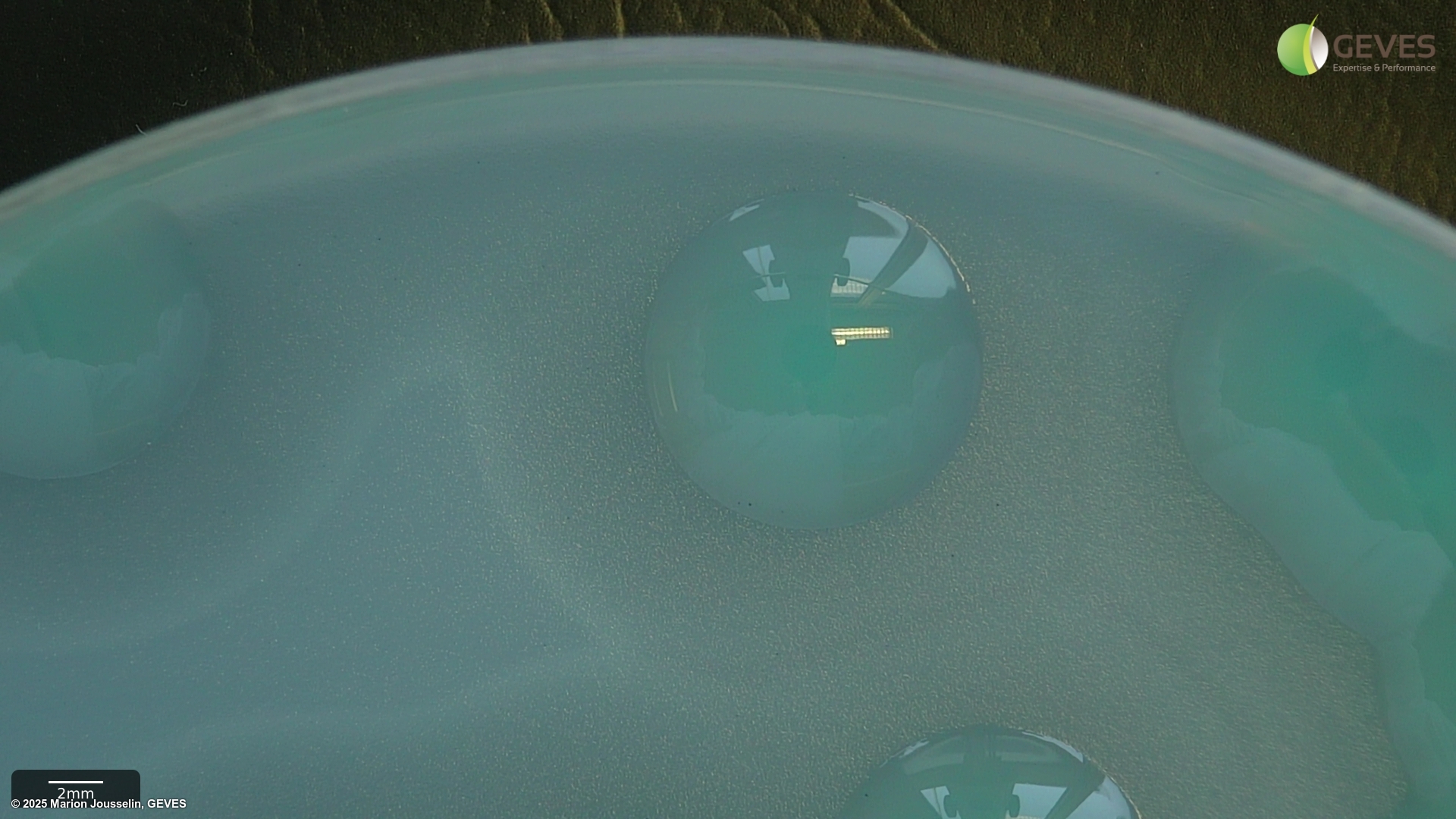
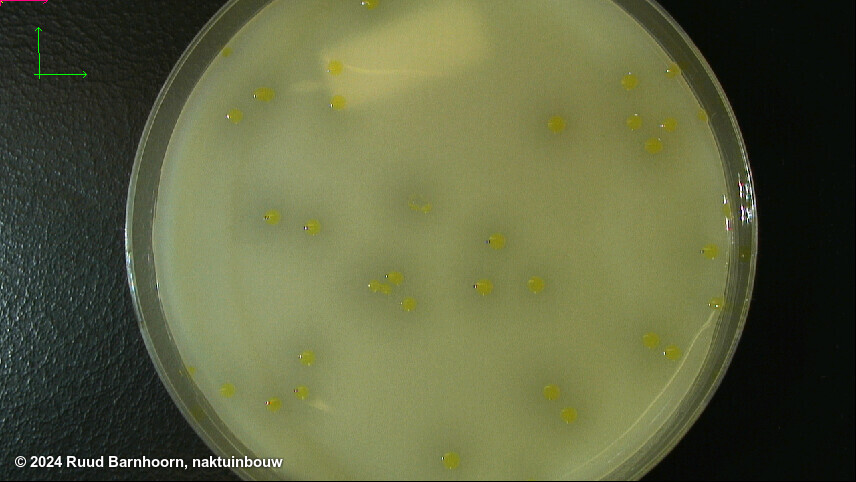
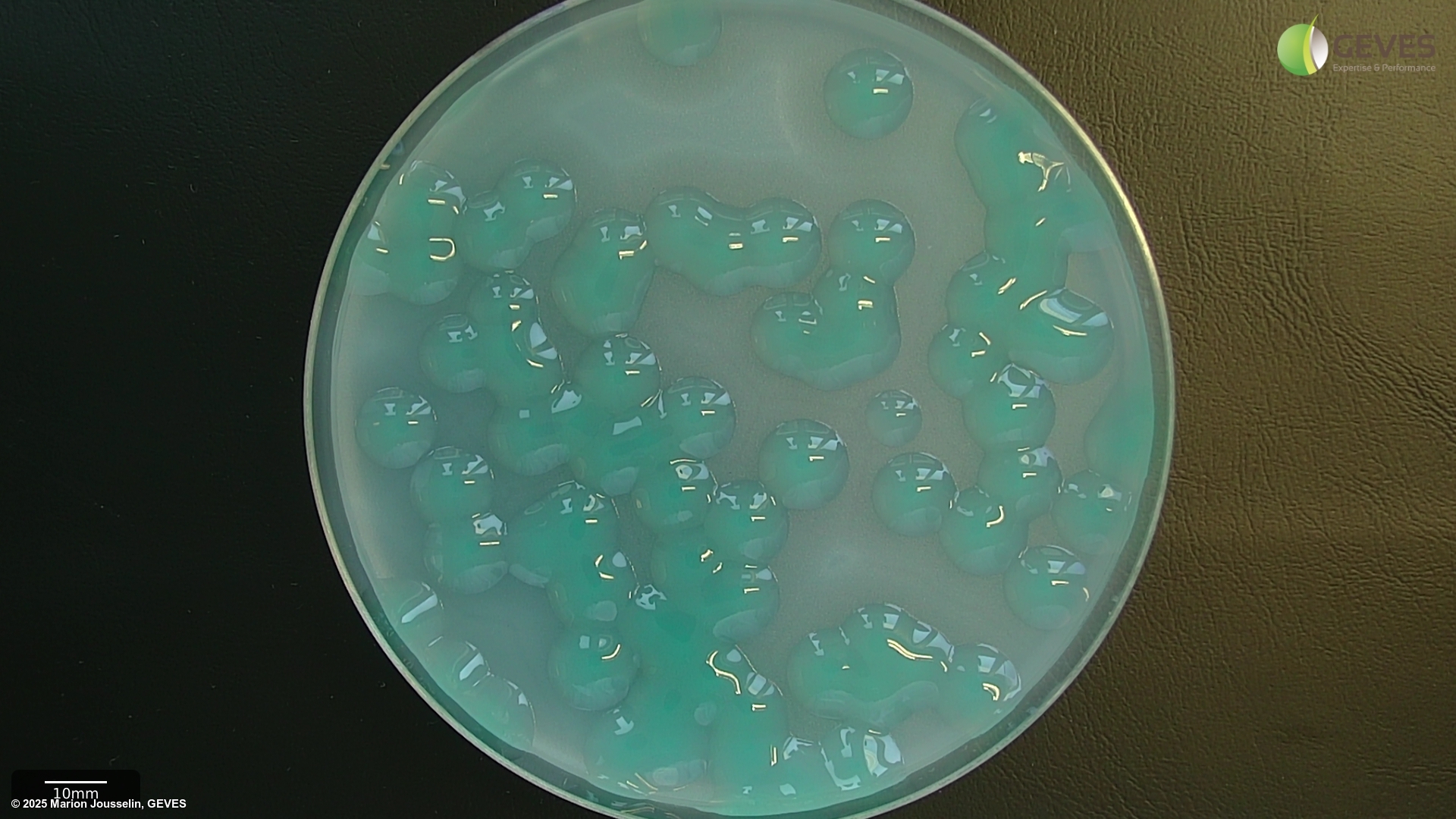
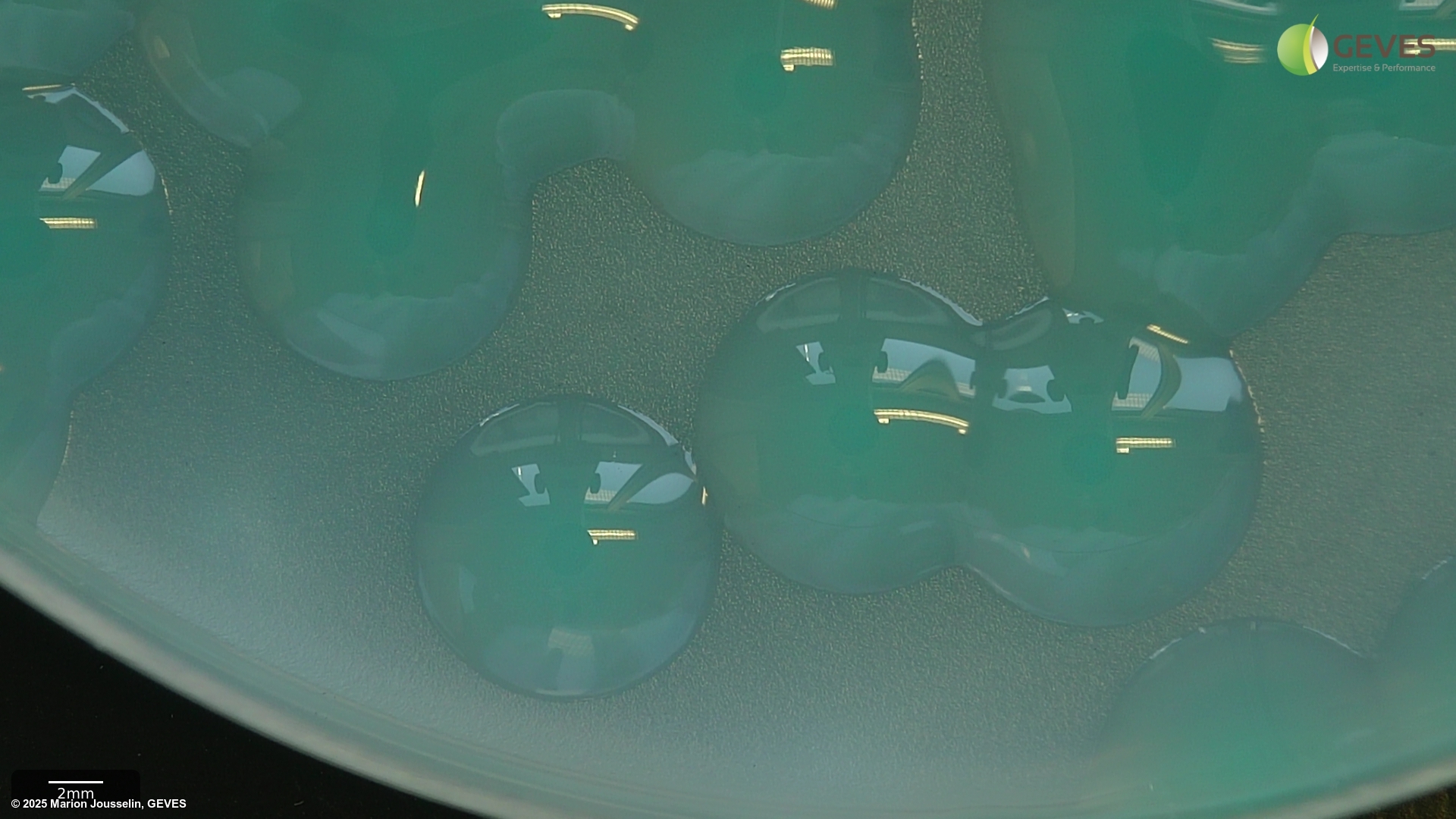
On FS after 3-4 days, Xcc colonies are small, pale green, mucoid and surrounded by a zone of starch hydrolysis. The zone appears as a halo that may be easier to see with a black background. Colonies may show marked variation in size and may be visible after 3 days, if not, incubate for an additional day.
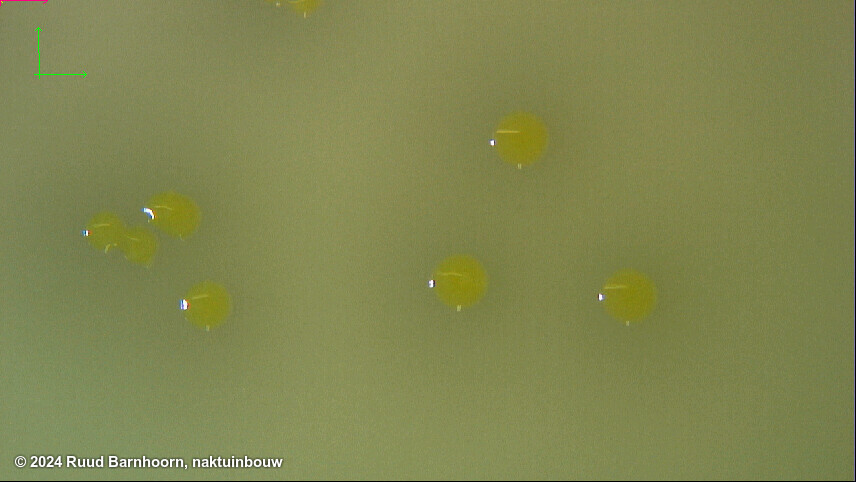
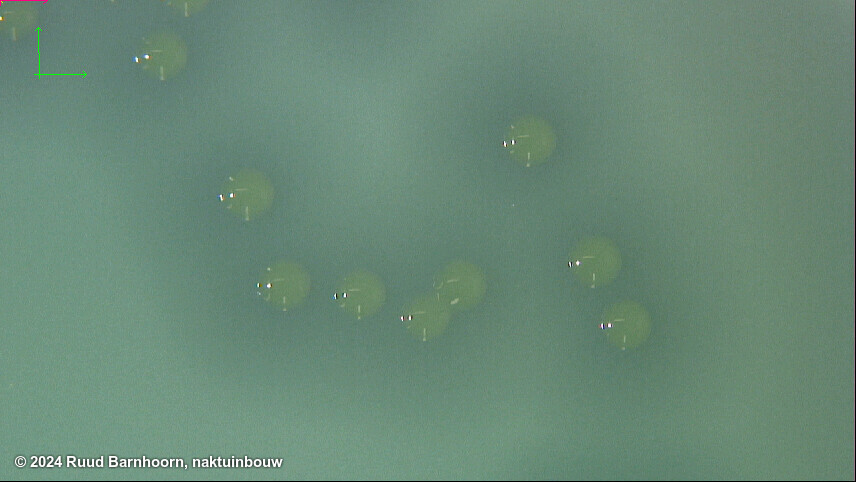
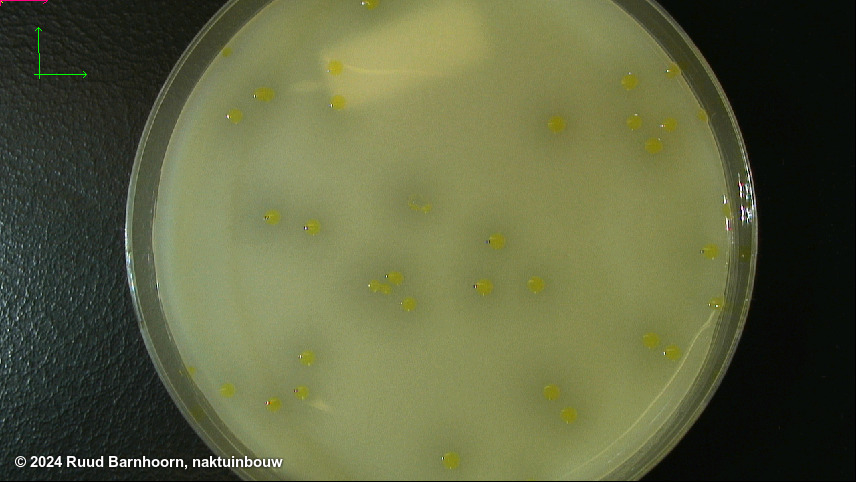
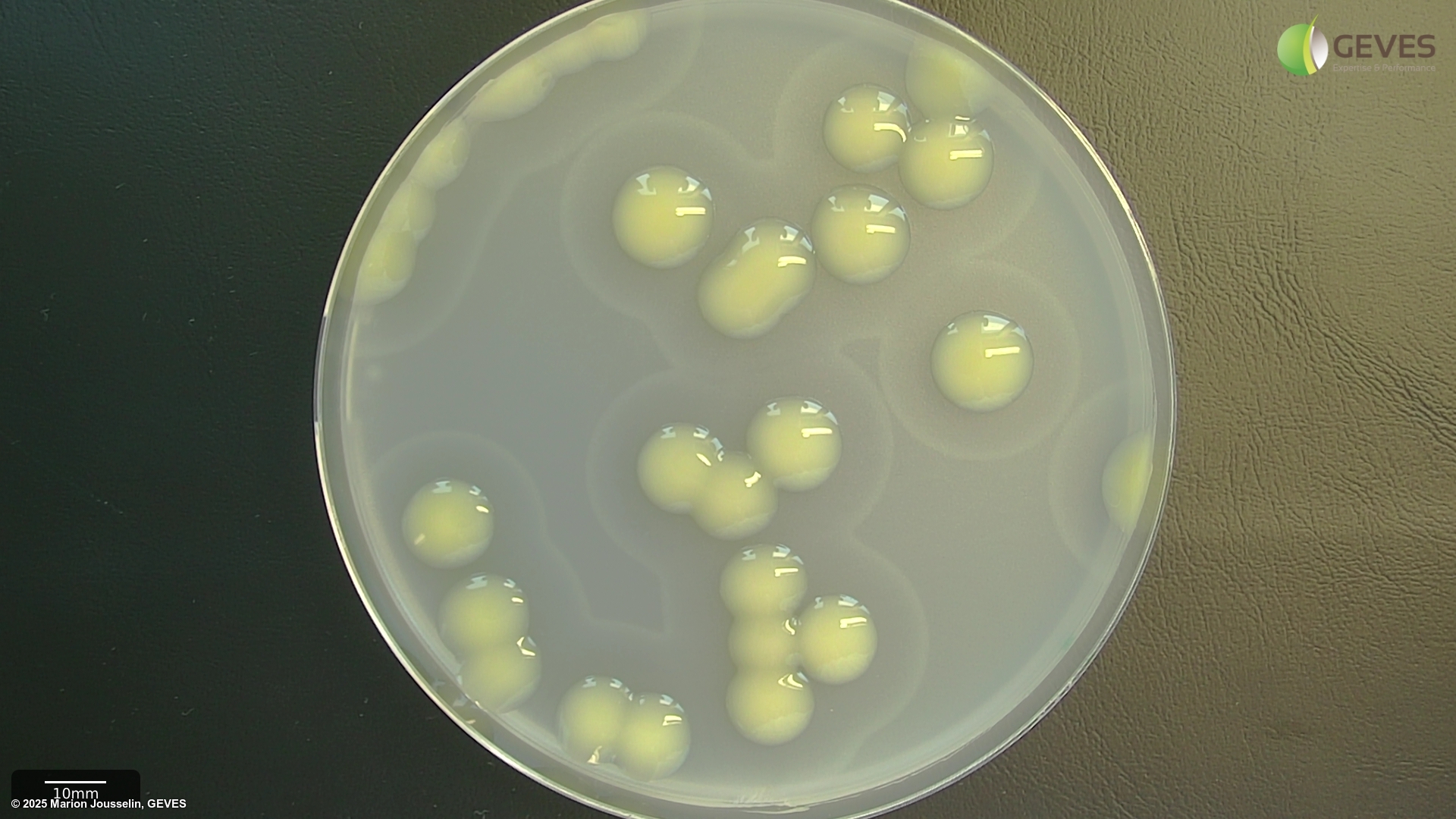
On mCS20ABN after 3-4 days, Xcc colonies are pale yellow, mucoid and surrounded by a zone of starch hydrolysis. Colonies may show marked variation in size. Depending on the number of colonies present, it may be easier to evaluate plates after 3 d, before coalescence of starch hydrolysis zones, which can make it more difficult to identify suspect colonies.
Tip: incubating plates at 4C for several hours before recording may result in sharper zones of starch hydrolysis, with some starch sources.
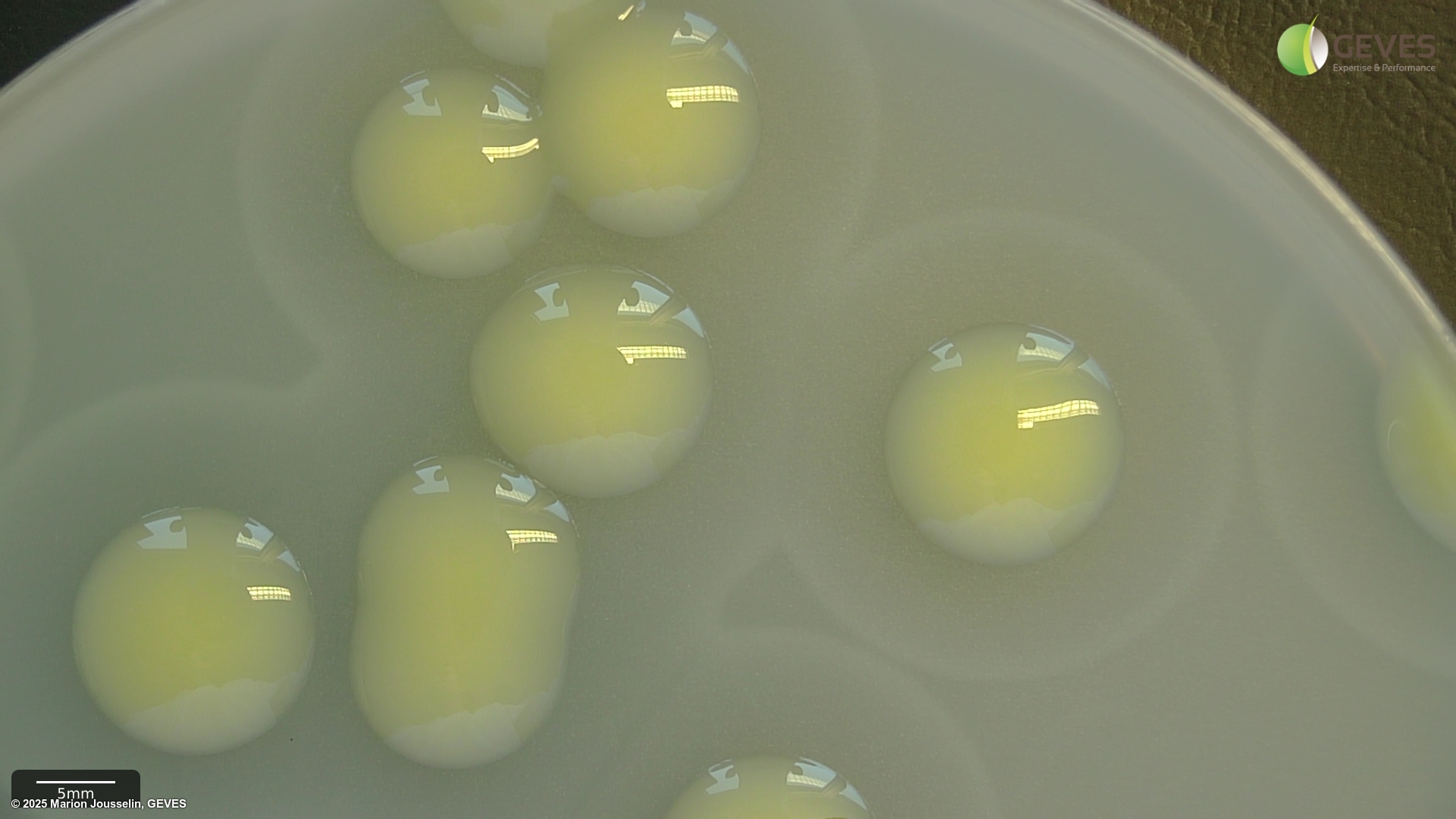
On YDC, subcultured colonies should be pale yellow and mucoid/fluidal after 48 hrs at 30C incubation.
For plant pathogenicity test, grow seedlings of a Brassica cultivar known to be susceptible to all races of Xcc (eg. cabbage cv. Wirosa, see Vicente et al., 2001) until at least 3-4 true leaf stage. After innoculation, examine plants for appearance of typical progressive V-shaped, yellow/nectrotic lesions with blackened veisn after 10-14 days. Symptoms may be visible earlier on, depending on temperature and isolate aggressiveness.