Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. phaseoli
Overview
|
Scientific name
|
Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. phaseoli |
|
Genus
|
Xanthomonas |
|
EPPO code
|
XANTPH |
|
Common name
|
Common Bacterial Blight of Bean |
|
Synonyms
|
Pseudomonas phaseoli |
Description
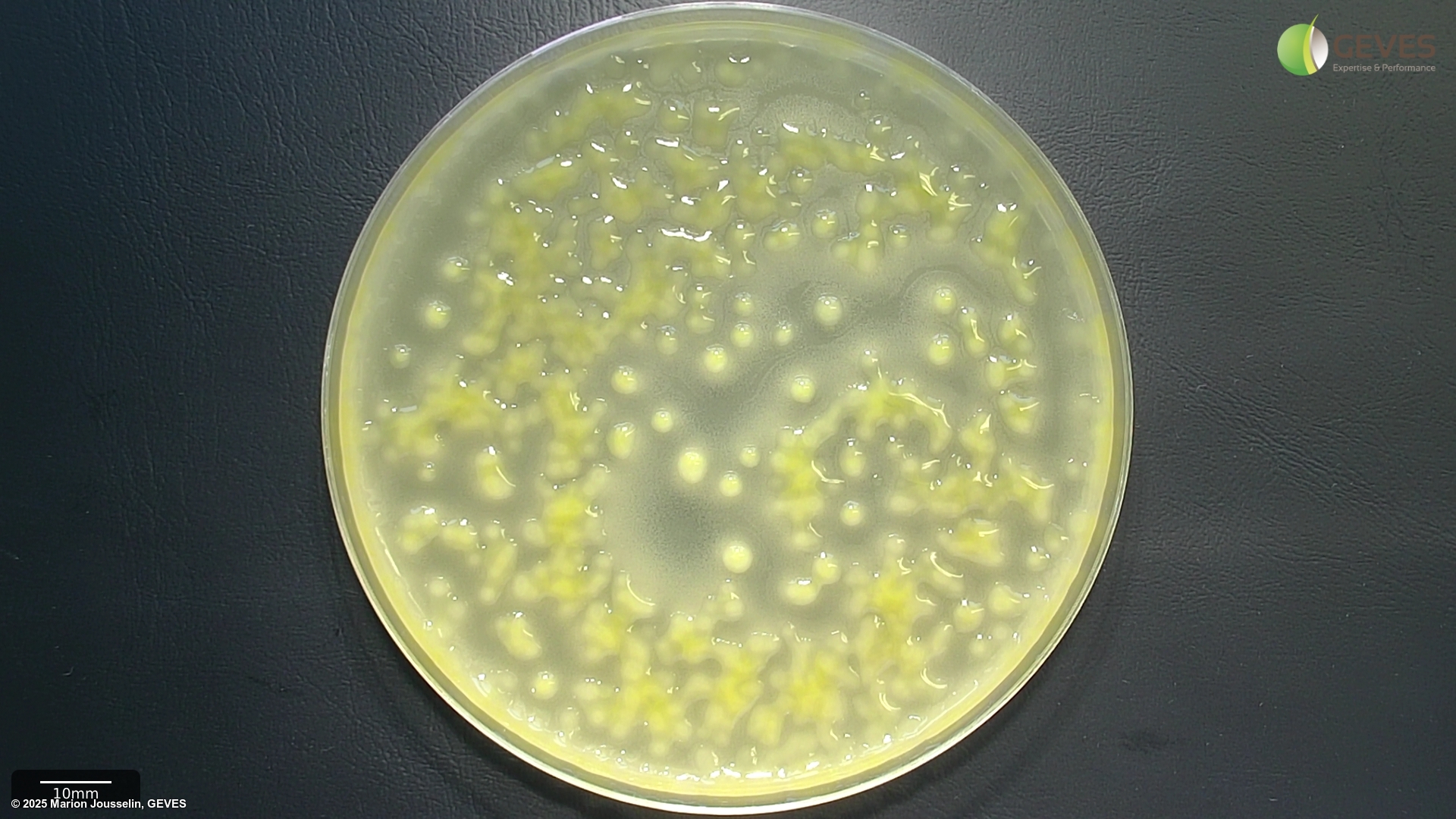
From ISTA method 7-021:
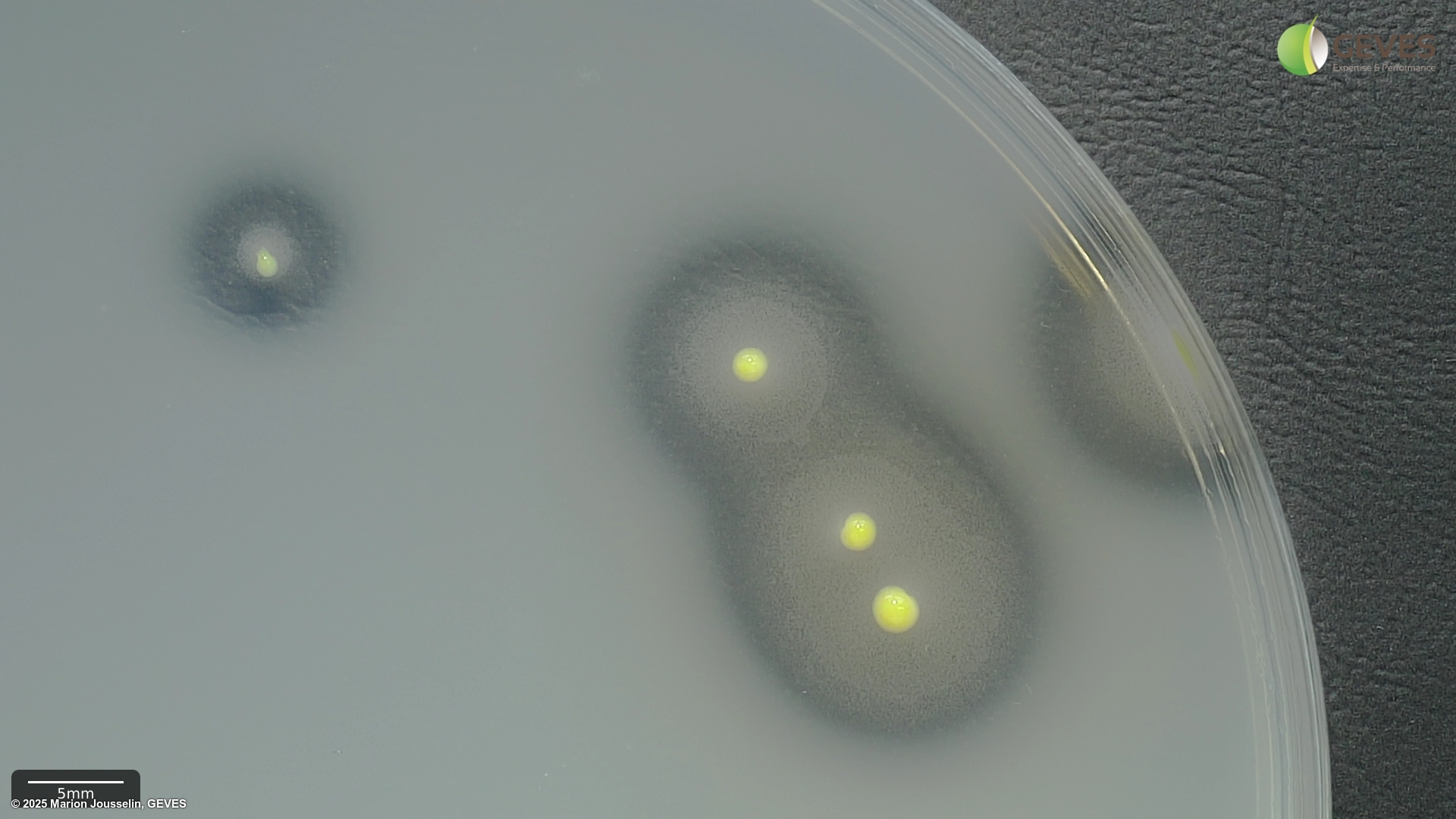
AFter 4-5 days on MT, Xap colonies are yellow distinguished by two zones of hydrolysis; a large clear zone of casein hydrolysis and a smaller milky zone of Tween 80 lysis. The fuscans of XAP colonies produce a brown diffusible pigment. If not visible after 4 days, incubate for an additional day. Often the fuscans type colonies show Tween 80 lysis.The colony size and colour can differ within a sample.
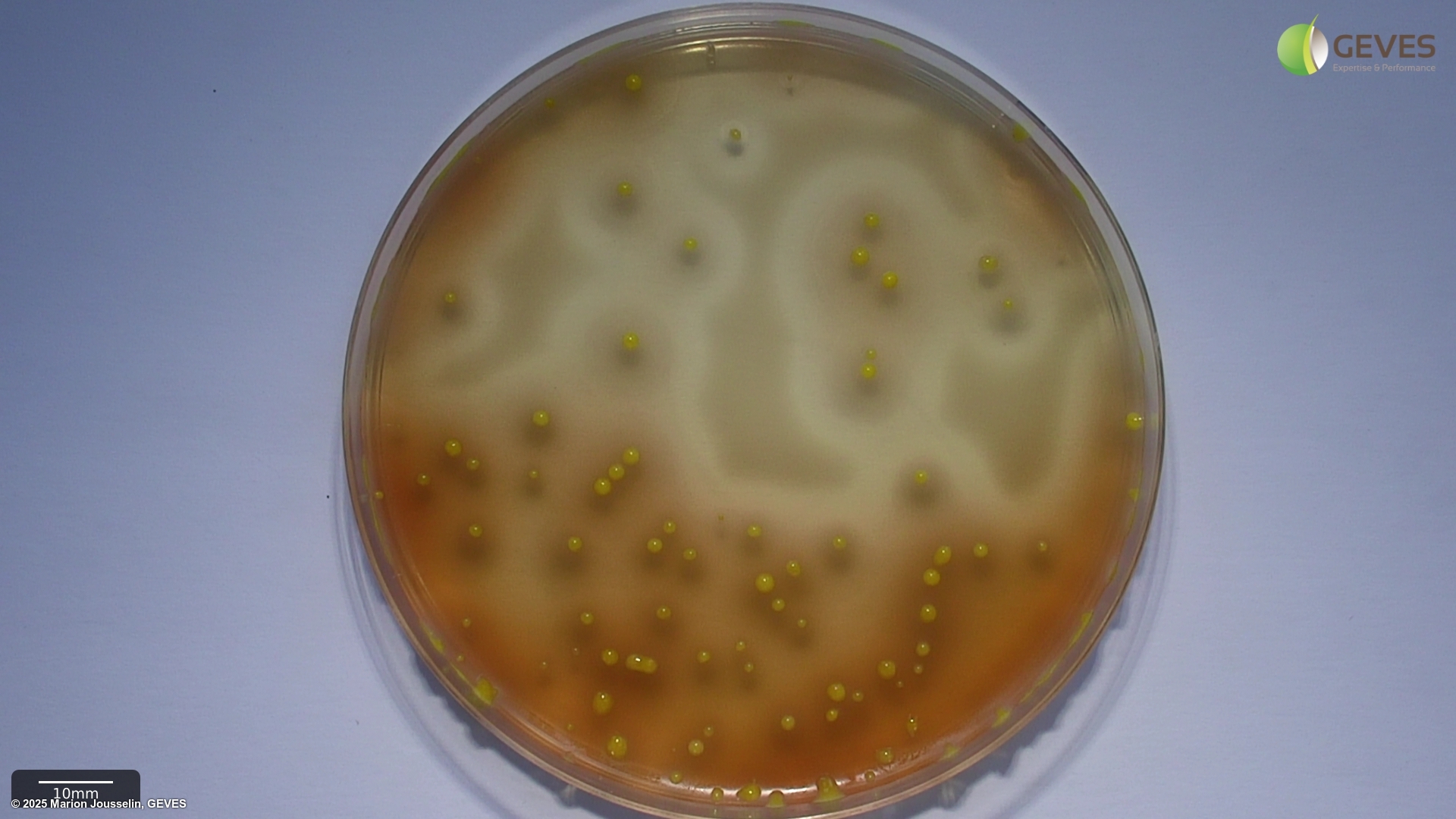
After 4-5 days on XCP1, Xap colonies are yellow, glistening and surrounded by a clear zone of starch hydrolysis. The fuscans of Xap colonies produce a brown diffusible pigment after 5 days of incubation. Often the fuscans type colonies show Tween 80 lysis. The colony size and colour can differ within a sample.
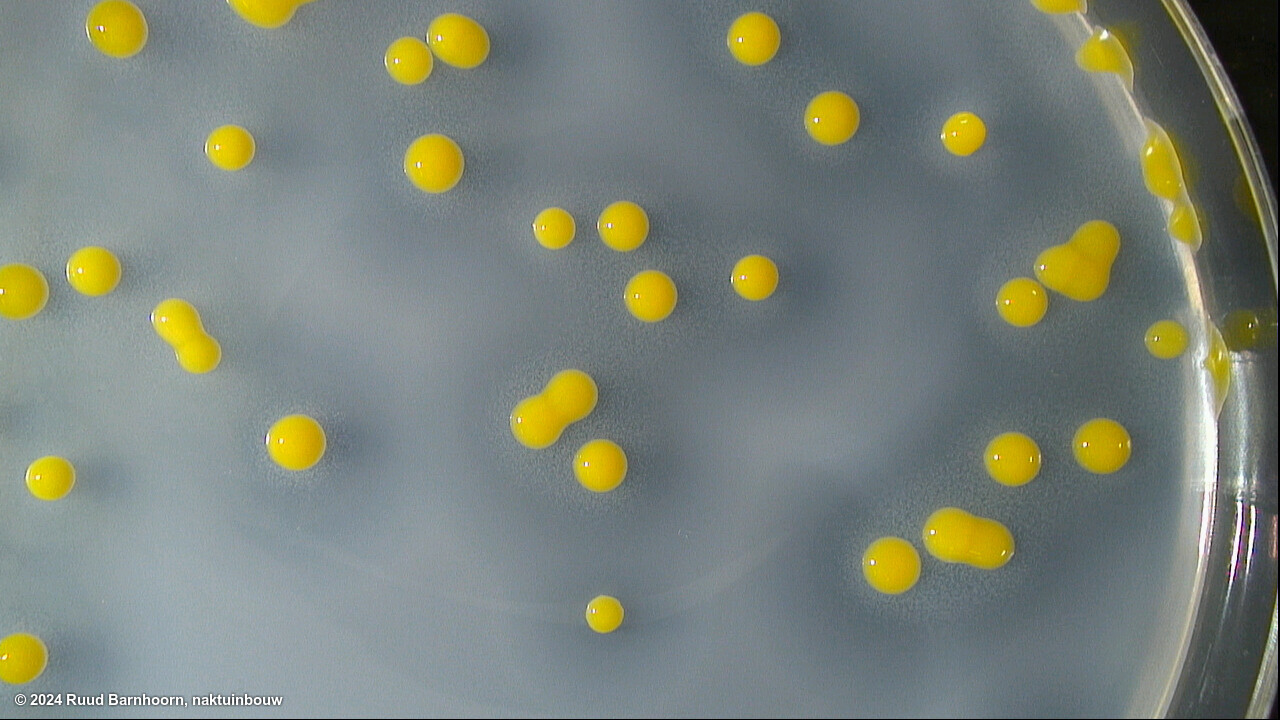
Suspected colonies, when subcultured on YDC, will be yellow and mucoid in appearance.
Pathogenicity test should be done on a bean seedling of a cultivar known to be susceptible to all races of Xap (e.g. Michelet or Contender at 20-30C) until the fist leaf is just visible. After innoculation, typical symptoms include dark green water-soaked lesions at the point of entry. Lesions can become red-brown, elongate extending into the stem causing slight to severe stem cracking. Symptoms for fuscans and non-fuscans are the same.