Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. phaseolicola
Overview
|
Scientific name
|
Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. phaseolicola |
|
Genus
|
Pseudomonas |
|
EPPO code
|
PSDMPH |
|
Common name
|
Bacterial Blight of Bean |
|
Synonyms
|
Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola |
Description
From ISTA 7-023 method:
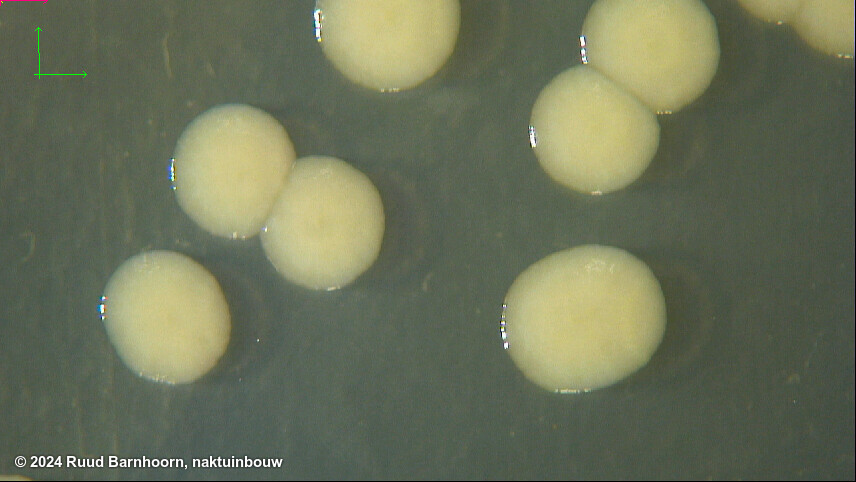
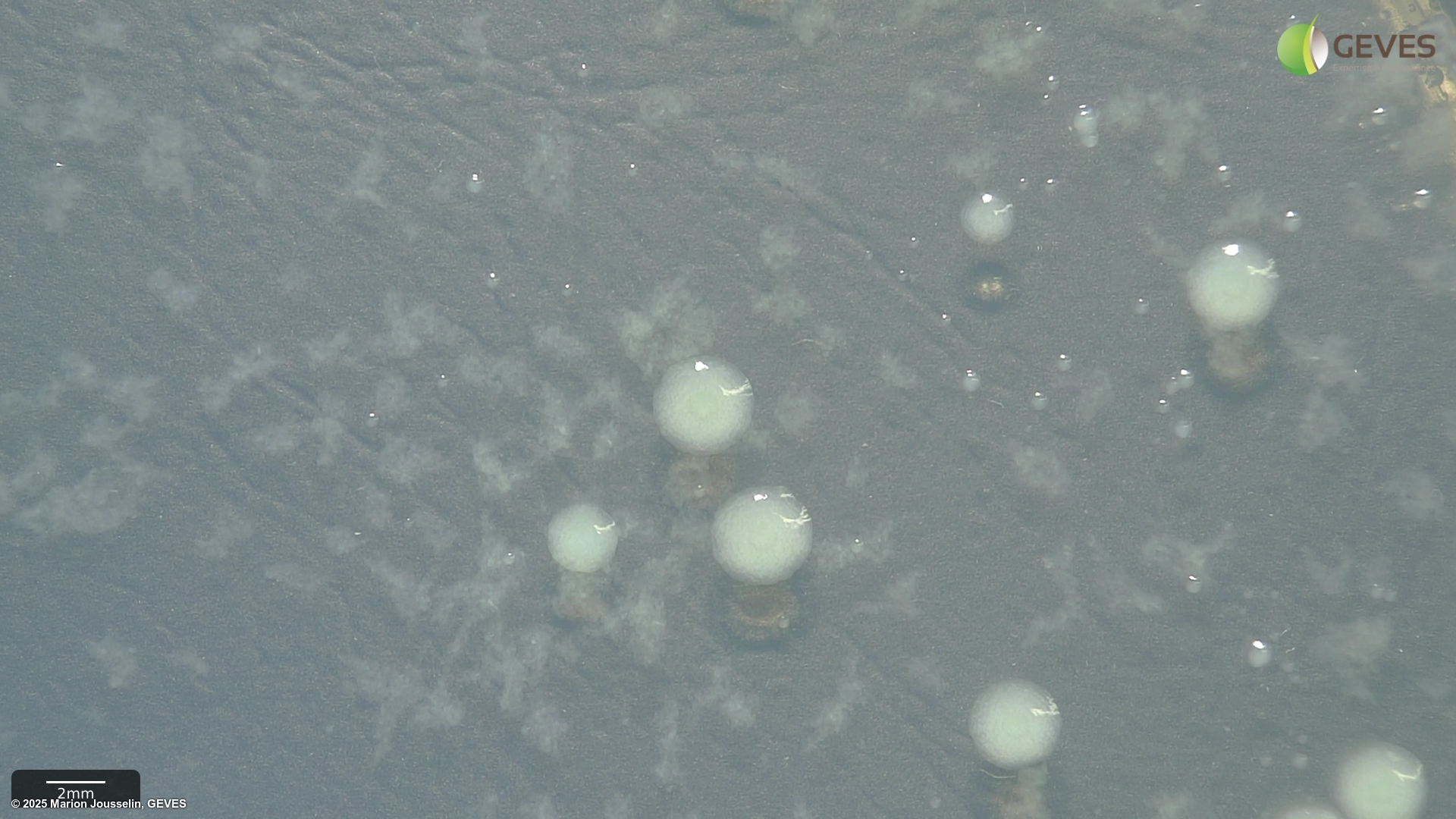
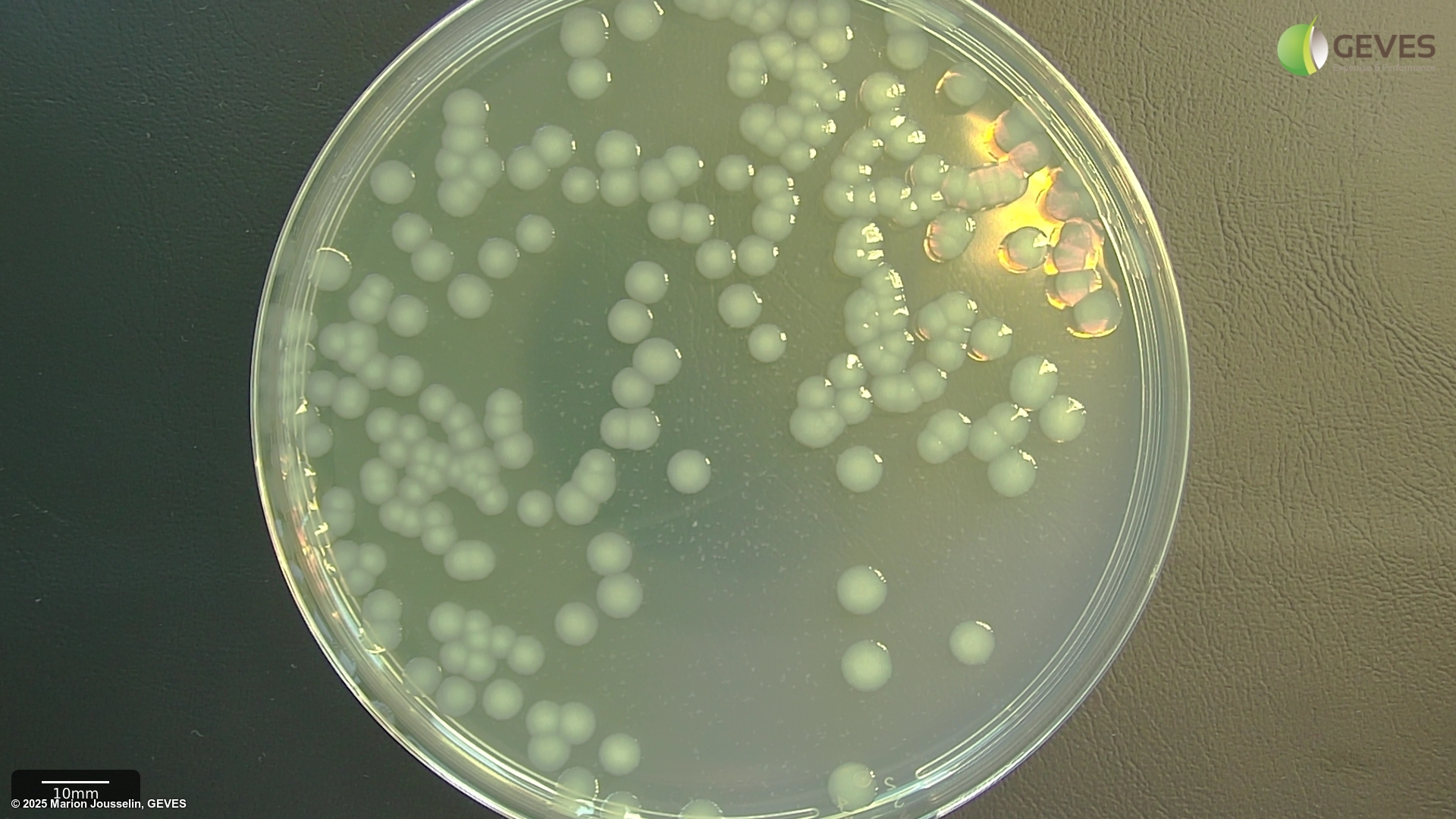
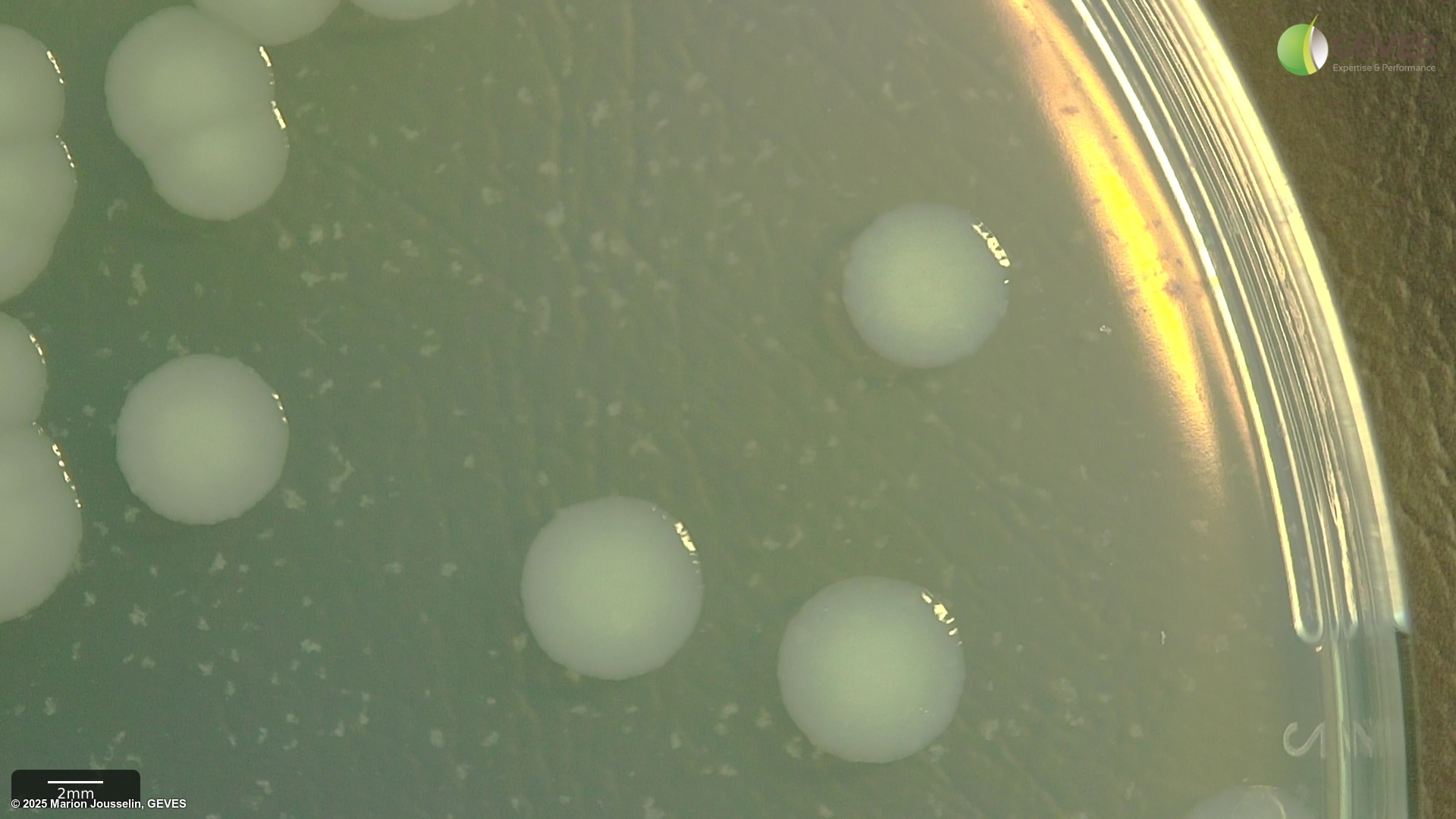
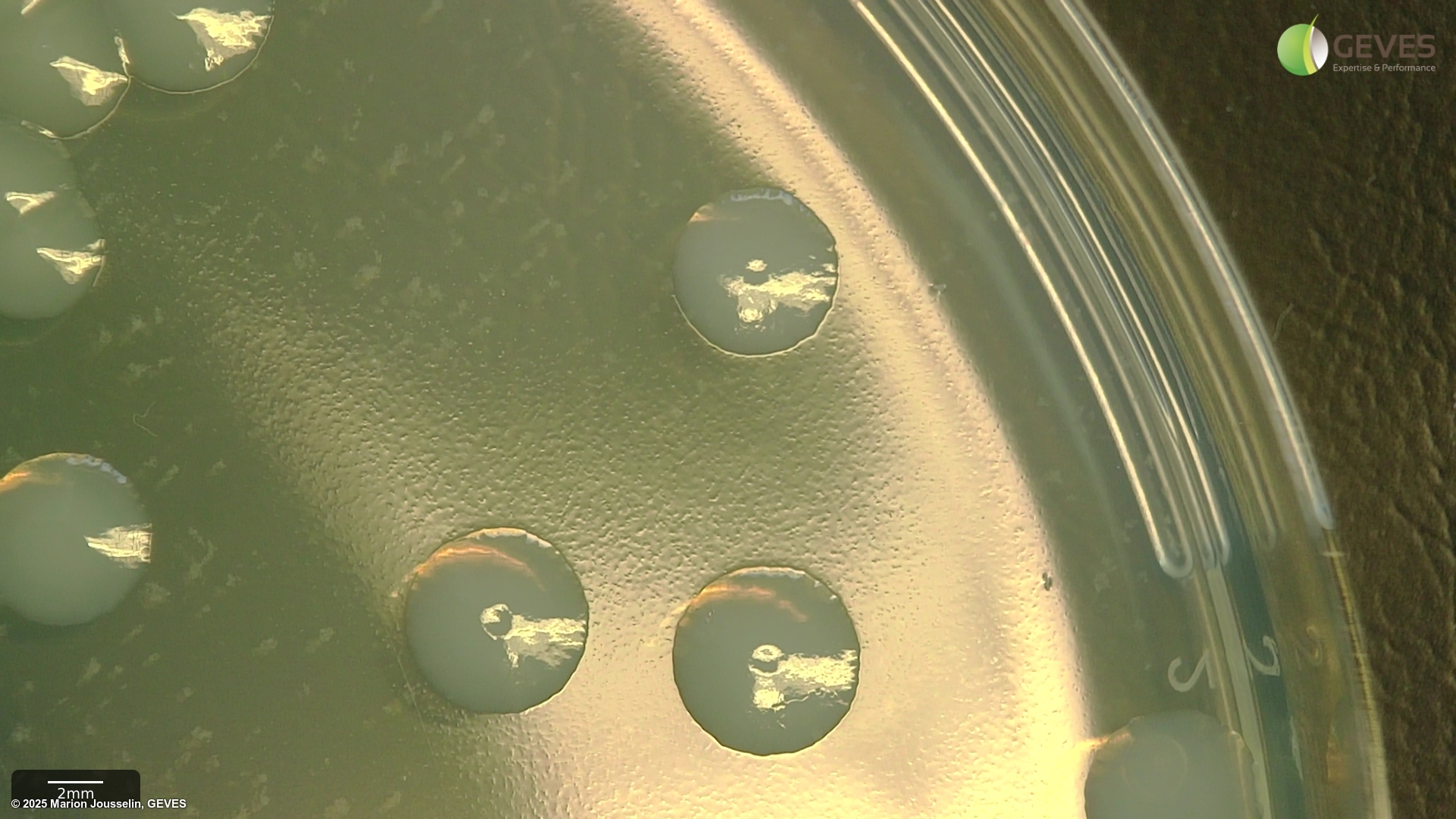
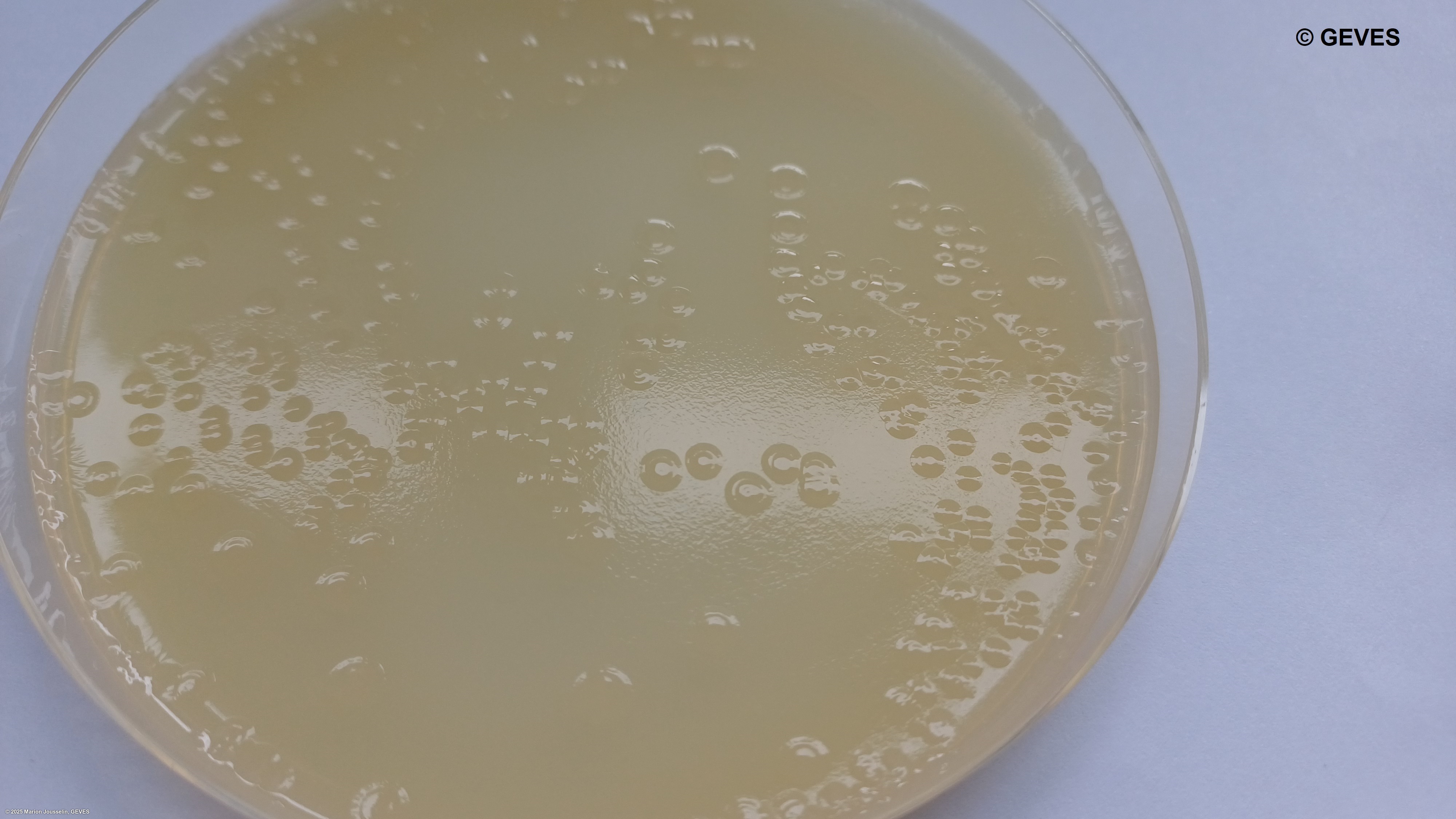
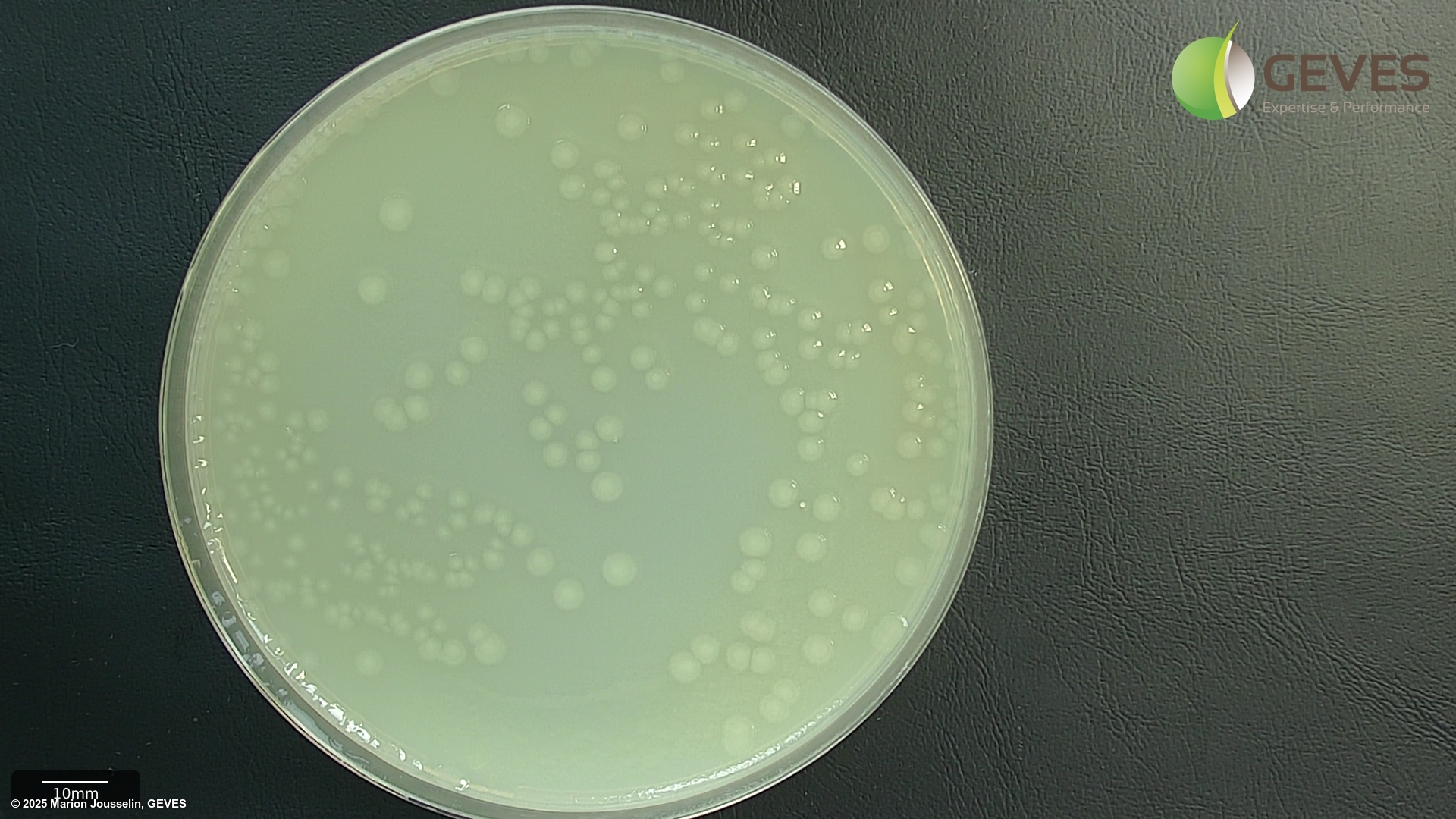
After 4-5 days on MT, Psp colonies are creamy white, flat, circular, 4.5-5 mm in diamter.
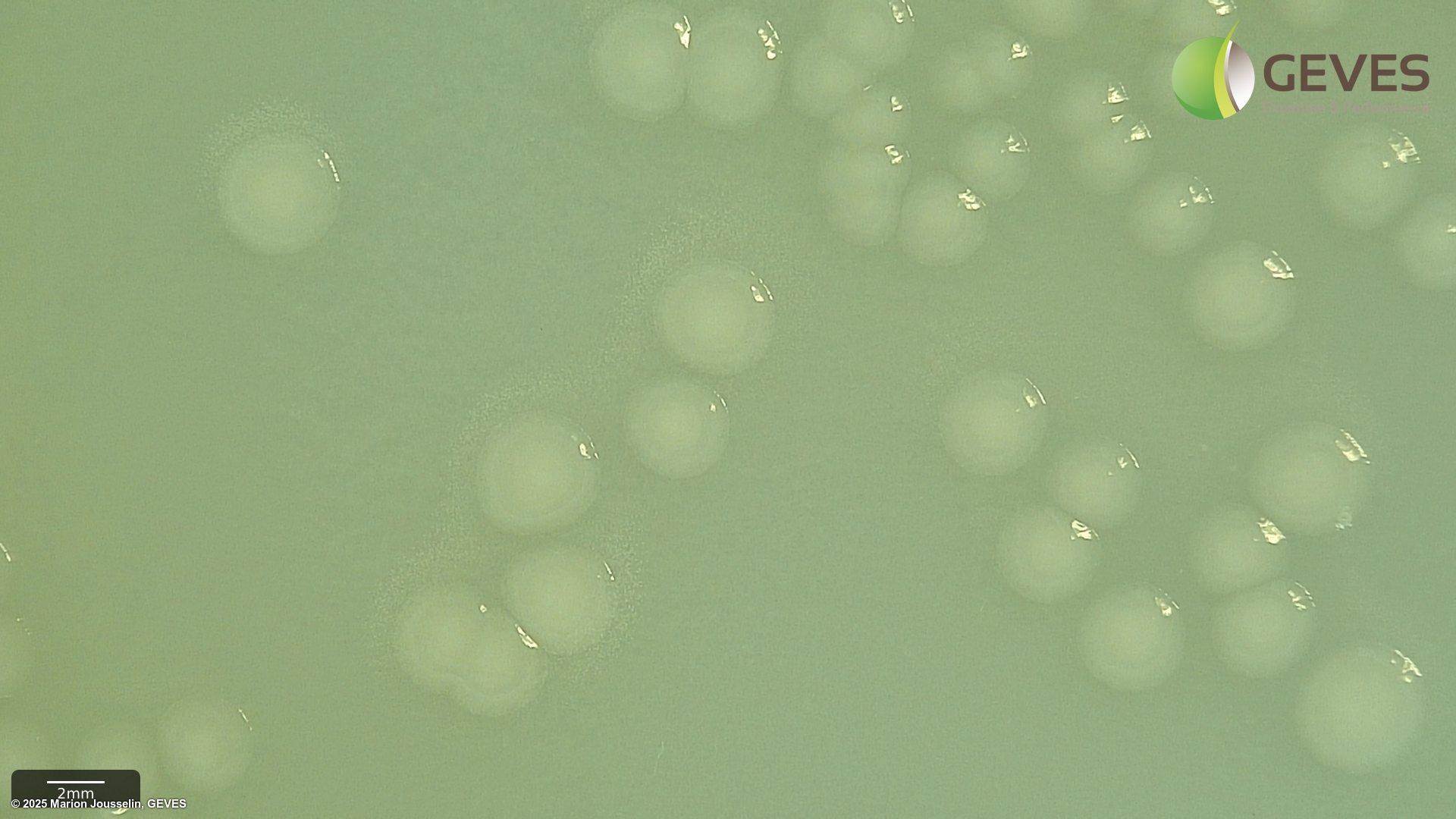
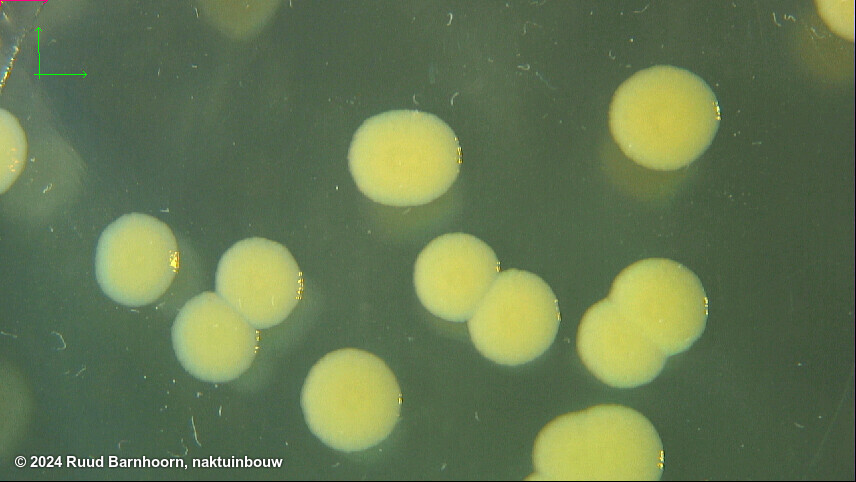
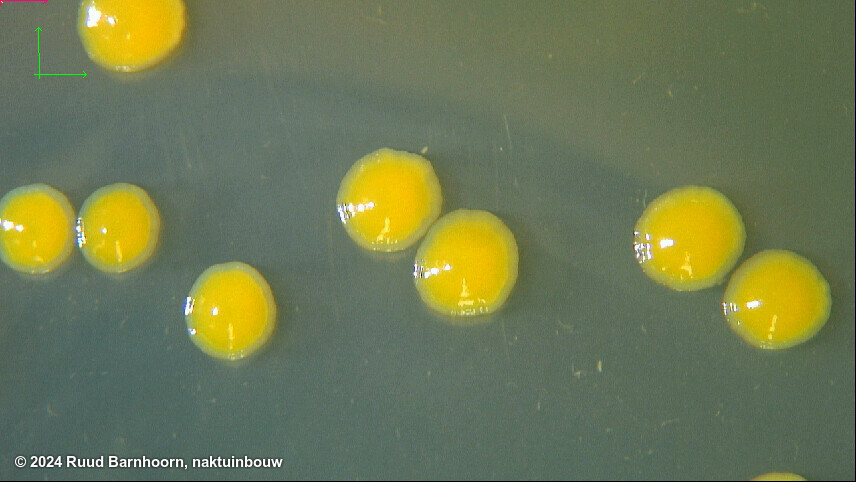
After 4-5 days on MSP, Psp colonies are circular, raised globose, glistening and light yellow with a less dense center. The medium around the colony turns light yellow after 3 days.
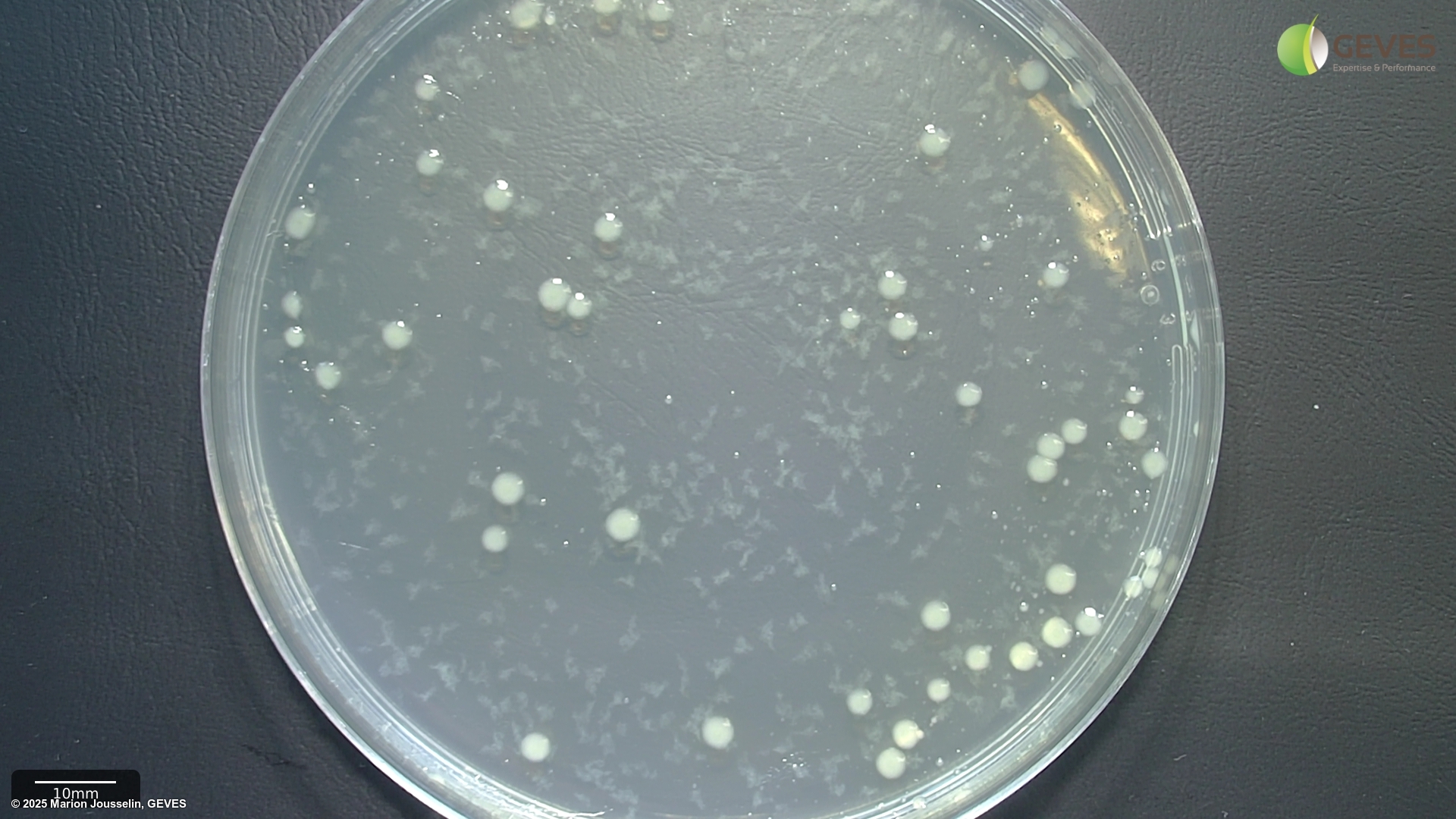
Subculture suspected colonies on KB. After 2-4 days on KB, Psp colonies into creamy or white circular and flat colonies.
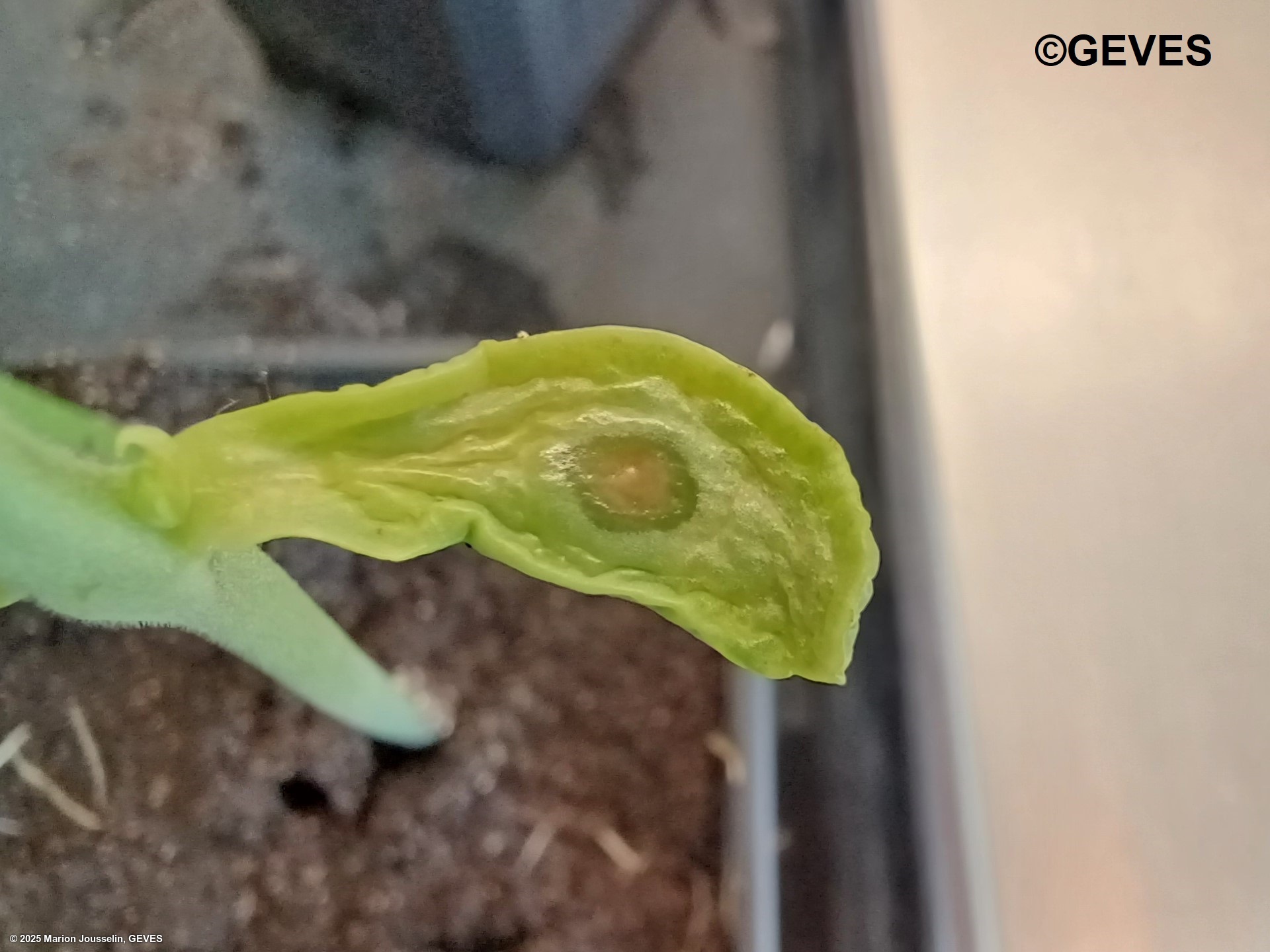
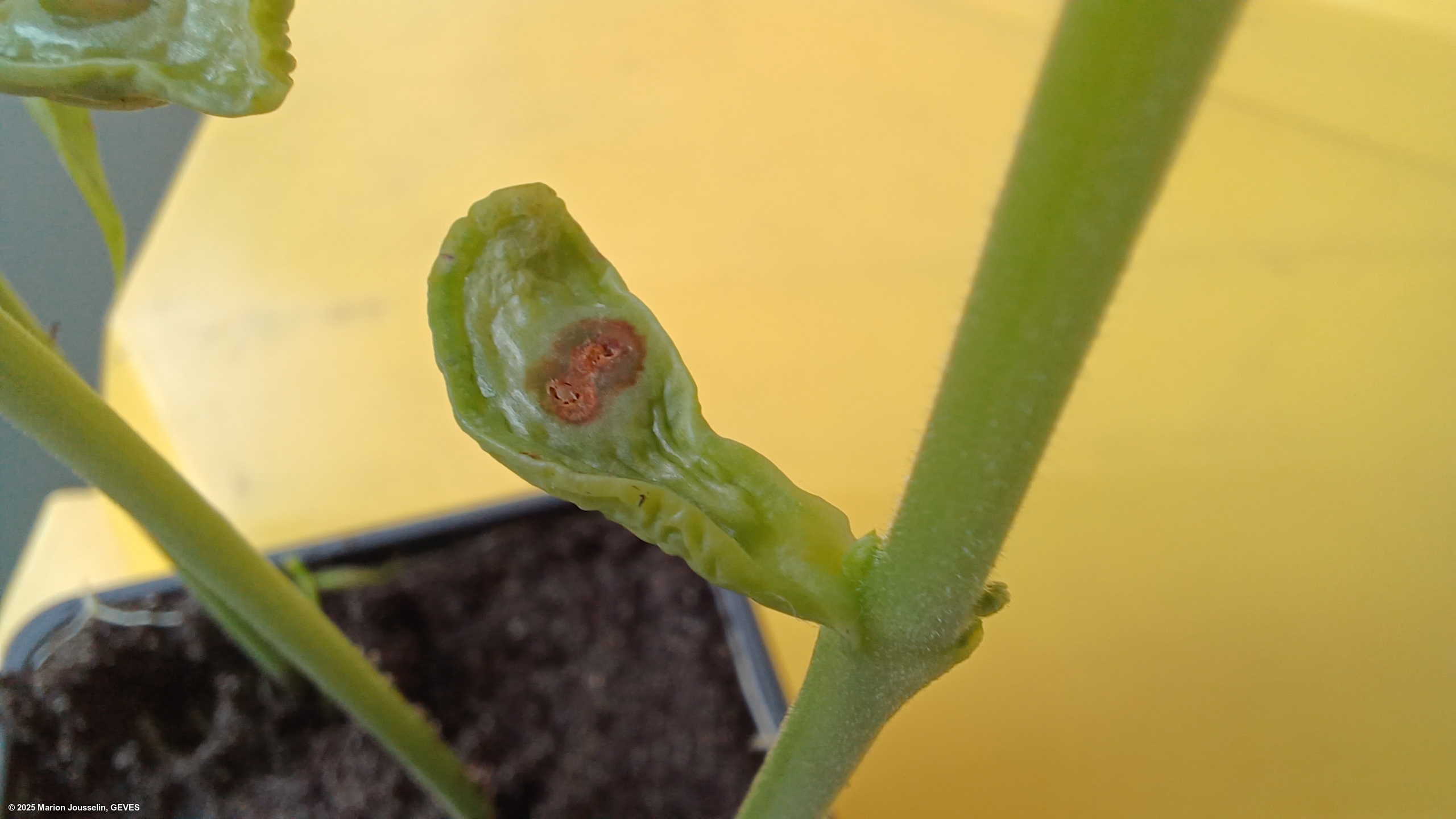
Pathogenicity tests should be carried out on a bean cultivar known to be susceptible to all races of Psp (e.g. cv. Helda). Innoculation can be done on the cotyledon, and seedlings should be transferred to damp soil for an additional 4-5 days at 20-25C with alternating light and dark cycles (12:12). Symptoms after 4-5 days should present as typical 'greasy' spots at the point of innoculation (flat inner sides). Reinspection may be carried out again at days 8-10, but the cotyledons may deteriorate too much.
From ISTA Working Sheet #65:
Direct inspection may be done on white coated cultivars with UV light (350-400nm) and presence of white fluorescent spots may indicate Psp infection. Reliability of this is LOW.
Detection via combined immuno-fluorescence microscopy and plating assay suggested. Colonies grown on King's medium B agar plates that produce blue or blue-green (but not bright green) fluorescent pigment can then be used in a pathogenicity test. Look for the typical grasy spots at innoculation points.